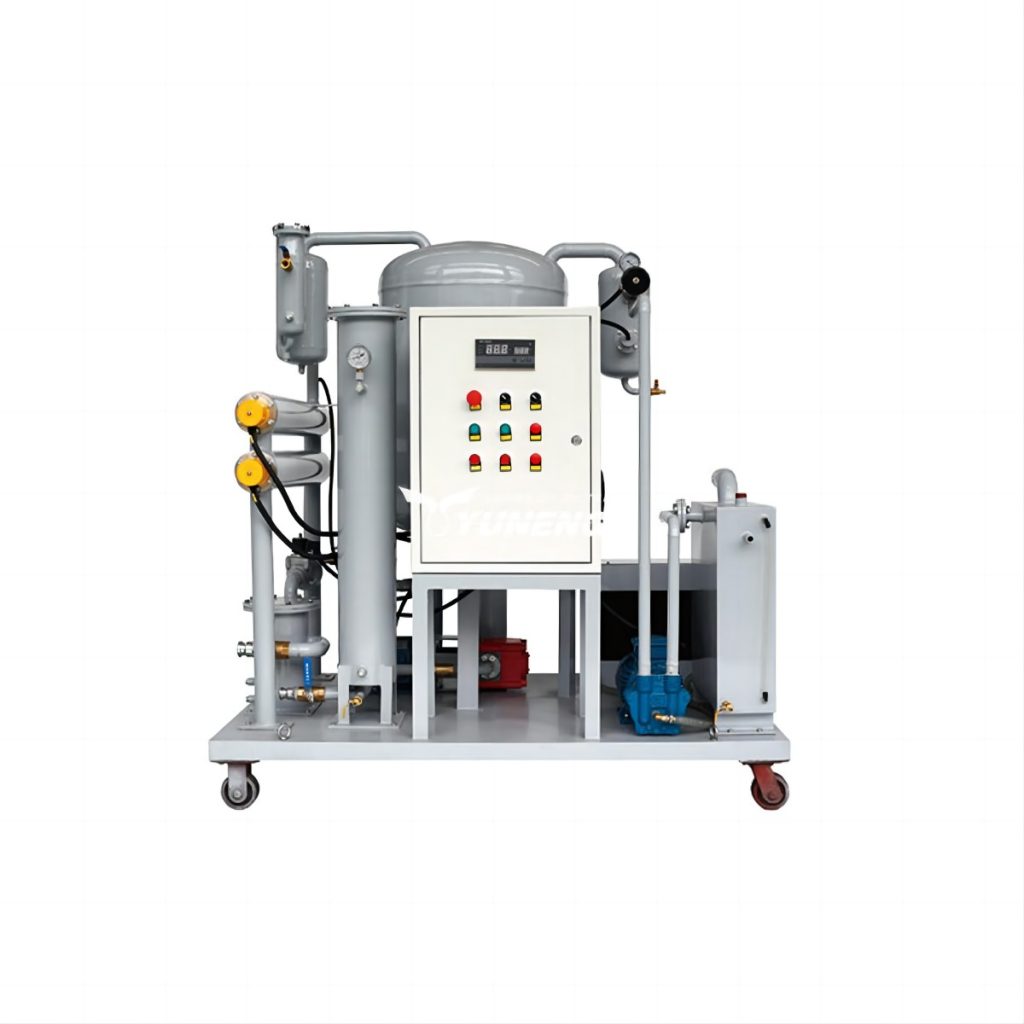
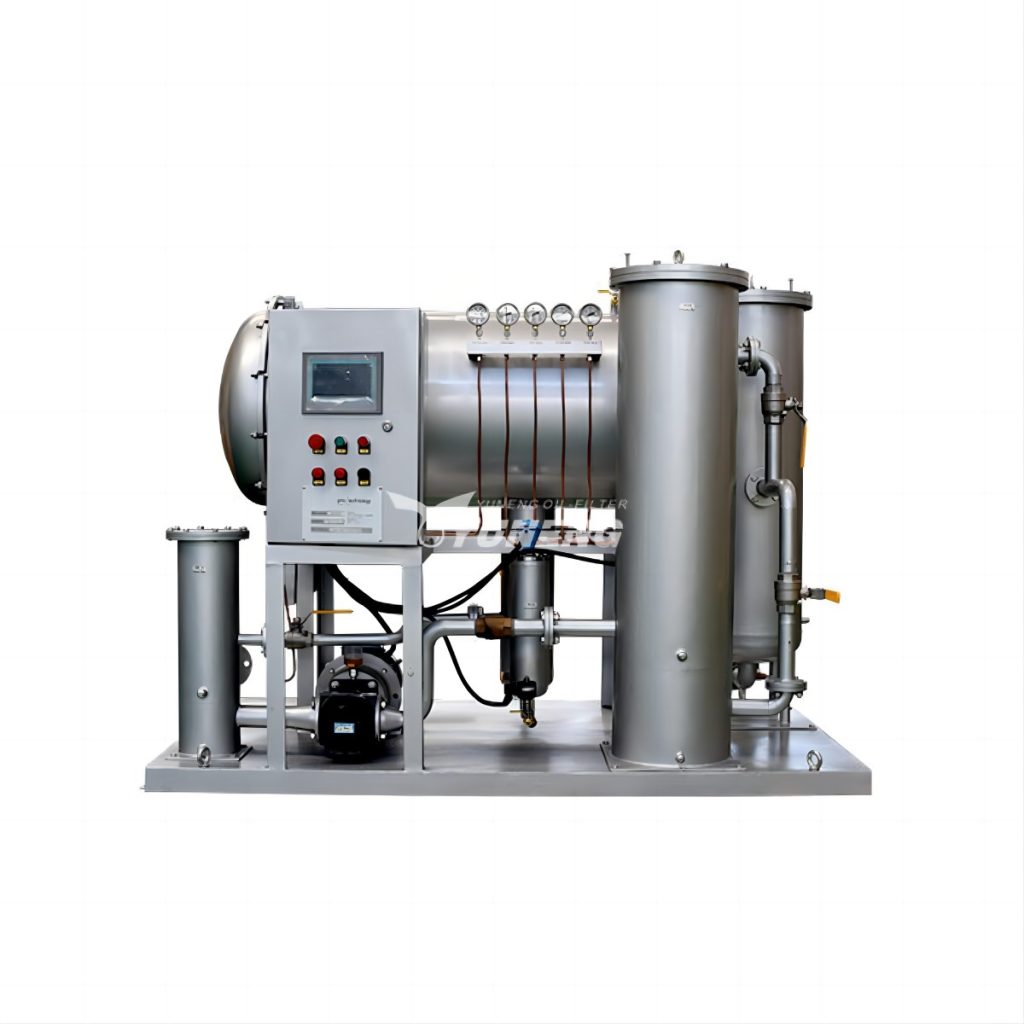
Common pollutants in turbine oil and the purification methods
Turbine oil serves as a critical component in the seamless and effective functioning of transformers and turbines, fulfilling roles as a lubricant, coolant, and insulator. Its presence guarantees the secure and dependable transmission of power. Nonetheless, with time, turbine oil may accumulate diverse impurities, undermining its efficacy and posing risks of equipment malfunction.
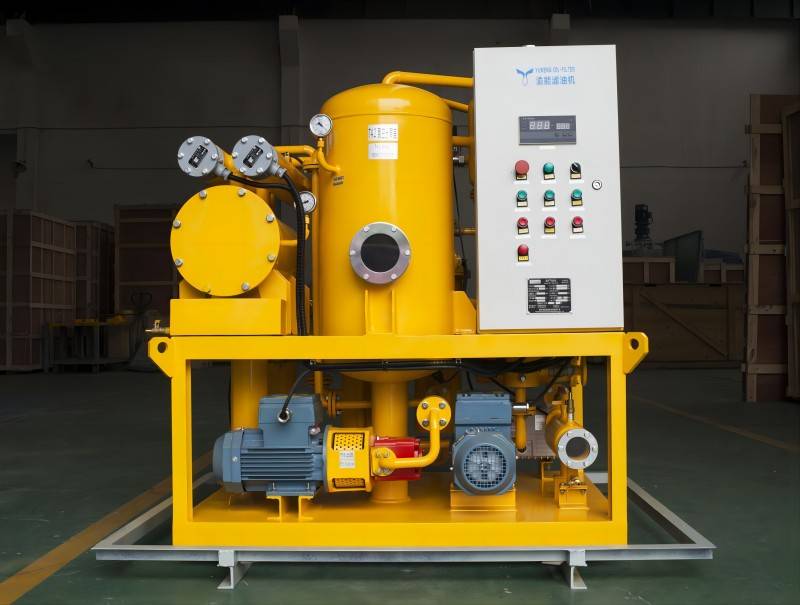

Common Turbine Oil pollutants
Several pollutants can infiltrate turbine oil, each with detrimental effects:
- Water: Moisture ingress stands as a significant adversary to turbine oil. Even minute quantities of water can hasten oil degradation through hydrolysis. This breakdown leads to varnish formation, heightened acidity, and diminished lubrication properties. Additionally, water can foster microbial growth within the oil system, further expediting its degradation process.
- Solid Particles: Dust, dirt, and metal wear debris are unwelcome intruders in turbine oil. Their presence can induce increased friction and wear on crucial components, resulting in sludge accumulation and compromised lubrication and heat transfer. Ultimately, this can diminish efficiency and escalate maintenance expenses.
- Oxidation Products: Exposure to air and elevated operating temperatures triggers oil oxidation. This chemical reaction yields sludge and other byproducts that elevate the oil’s viscosity. Thicker oil exhibits reduced flow capability, impeding its ability to lubricate and cool efficiently. Furthermore, oxidation compromises the oil’s insulating properties, heightening the likelihood of electrical breakdowns.
- Acids: Internal combustion stemming from arcing or partial discharge within the transformer can generate acids within the oil. These acidic pollutants accelerate the degradation process, fostering corrosion of metal components and diminishing the equipment’s overall lifespan.

Consequences of Untreated Turbine Oil
Neglecting turbine oil purification can lead to a cascade of problems that not only impact equipment health but also your bottom line in several significant ways:
- Reduced Efficiency: When turbine oil becomes contaminated, it increases friction within the transformer or turbine, subsequently raising operating temperatures. This diminished efficiency results in lower power output and heightened energy consumption, ultimately affecting operational costs.
- Increased Maintenance Costs: Contaminated oil accelerates wear and tear within the machinery, necessitating more frequent and intensive maintenance efforts. Addressing issues such as sludge buildup and replacing worn components becomes a recurring expense, significantly inflating maintenance budgets.
- Risk of Equipment Failure: The presence of severe contamination poses serious risks to equipment integrity. Sludge accumulation can obstruct filters and valves, impeding oil flow and potentially leading to catastrophic equipment failure. In extreme cases, acidic pollutants can corrode critical components, precipitating sudden breakdowns that incur substantial repair or replacement costs.
- Shortened Equipment Lifespan: Unpurified oil undergoes accelerated degradation, shortening the operational lifespan of transformers and turbines. This premature aging necessitates earlier equipment replacements, imposing significant capital expenditures and disrupting long-term budget planning.
In conclusion, neglecting turbine oil purification not only compromises equipment performance and reliability but also imposes financial burdens through increased operational costs, maintenance expenses, and the premature replacement of essential machinery. Prioritizing regular oil purification and maintenance routines is essential to mitigate these risks and ensure the sustained efficiency and longevity of your equipment assets.
How Turbine Oil Filtration Machine Eliminates pollutants
Turbine oil purification machines, commonly referred to as oil filter machines, are indispensable tools in maintaining the efficiency and longevity of various industrial equipment such as turbines and transformers. These machines employ a range of sophisticated technologies to eliminate harmful pollutants from the oil, thereby restoring its original properties and enhancing its performance. Here, we delve into the intricacies of these technologies and their role in the purification process:
- Coagulation: One of the primary methods employed by turbine oil purification machines is coagulation. This process involves introducing a specialized absorbent clay, often Fuller’s earth, into the contaminated oil. The clay particles possess a high affinity for water and oxidation by-products such as varnish and sludge precursors. As the clay interacts with the oil, it selectively absorbs these impurities, forming larger aggregates. Once saturated with pollutants, the clay is easily separated from the oil through filtration, leaving behind cleaner and rejuvenated oil.
- Filtration: Multi-stage filtration plays a pivotal role in the purification process by effectively removing solid particles suspended in the oil. These particles can range from fine dust and dirt to more substantial metal debris, all of which have the potential to cause abrasive wear and tear on turbine and transformer components. The filtration process typically involves passing the oil through a series of increasingly finer filters, ensuring that even the minutest pollutants are captured and removed. By maintaining clean oil, filtration helps safeguard equipment from premature failure and ensures smooth operation.
- Vacuum Dehydration: Another crucial aspect of turbine oil purification is vacuum dehydration. This technology utilizes a vacuum chamber to create a controlled environment with significantly reduced pressure. Under these conditions, water molecules dissolved in the oil undergo vaporization, allowing them to be efficiently extracted from the oil stream. By removing moisture, vacuum dehydration mitigates the risk of hydrolysis and other water-induced degradation processes. This not only helps preserve the oil’s chemical stability but also enhances its dielectric strength, crucial for insulating electrical equipment against breakdowns.
- Degassing: In addition to water, turbine oil often contains dissolved gases such as air and nitrogen, which can compromise its performance and longevity. Degassing is a process employed by purification machines to eliminate these undesirable gases. Similar to vacuum dehydration, degassing utilizes a vacuum environment to facilitate the extraction of dissolved gases from the oil. By removing air and nitrogen, this process minimizes the risk of oxidation and degradation, thereby preserving the oil’s insulating properties and prolonging the lifespan of equipment.
By integrating these various purification techniques in a synergistic manner, turbine oil purification machines effectively cleanse the oil, restoring it to its pristine state and ensuring optimal performance of industrial equipment. Whether in power plants, manufacturing facilities, or other critical operations, the reliability and efficiency of turbines and transformers depend significantly on the quality of the oil circulating within them. With advanced purification technologies at their disposal, industries can uphold stringent maintenance standards, prolong equipment lifespan, and mitigate the risk of costly downtime.
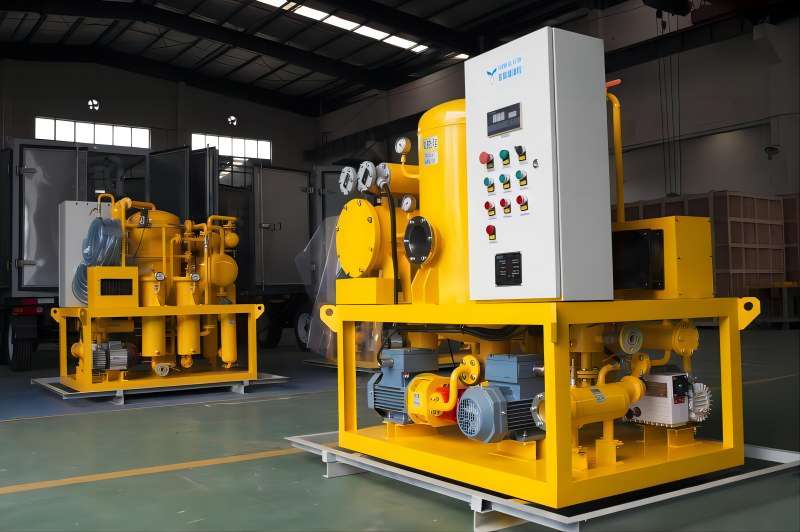

Benefits of Using Turbine Oil Filtration Machines
Regular turbine oil purification is not just a maintenance task; it’s a strategic investment that offers a multitude of benefits, all of which contribute to a healthy bottom line and reliable power generation. Let’s explore these advantages in greater detail:
- Extended Equipment Life: Perhaps the most evident benefit of regular turbine oil purification is the extension of equipment lifespan. Clean, purified oil serves as a protective barrier against friction and corrosion, minimizing wear and tear on vital components within transformers and turbines. By reducing mechanical stress and preserving the integrity of critical parts, purified oil significantly prolongs the operational life of these assets. Consequently, businesses can avoid the hefty expense of premature equipment replacement, leading to substantial cost savings over time.
- Improved Efficiency: Clean oil plays a pivotal role in optimizing the performance of transformers and turbines. With pollutants removed and lubrication properties restored, the equipment operates more efficiently, translating into increased power output. This enhanced efficiency not only boosts productivity but also results in lower energy consumption, reducing operational costs in the long run. By maximizing the utilization of available resources, businesses can achieve greater profitability while minimizing their environmental footprint.
- Reduced Maintenance Costs: Clean oil doesn’t just benefit equipment longevity; it also translates to reduced maintenance requirements and associated costs. By minimizing wear and tear, purified oil lowers the frequency of maintenance interventions, such as component replacements and repairs. Moreover, regular oil analysis as part of the purification process enables early detection of potential issues, allowing for proactive maintenance measures to be implemented. By addressing problems before they escalate into catastrophic failures, businesses can avoid costly downtime and emergency repair expenses, further bolstering their bottom line.
- Enhanced Equipment Reliability: Consistency is key when it comes to ensuring the reliable operation of transformers and turbines. Regular purification of turbine oil minimizes the accumulation of pollutants, reducing the risk of equipment breakdowns and unscheduled outages. This enhanced reliability is particularly crucial for industries that rely heavily on continuous power generation, such as manufacturing plants and data centers. By maintaining uninterrupted operation, businesses can uphold their commitments to customers and stakeholders, safeguarding their reputation and competitiveness in the market.
In summary, regular turbine oil purification offers a host of tangible benefits that go beyond mere maintenance. From extending equipment lifespan and improving efficiency to reducing maintenance costs and enhancing reliability, the investment in purification yields significant returns in terms of both financial savings and operational resilience. By prioritizing the health of their equipment through proactive maintenance practices, businesses can secure a sustainable and prosperous future in the ever-evolving landscape of power generation.
Conclusion
Turbine oil purification system is an essential preventative maintenance practice for maintaining the health of transformers and turbines. By proactively removing pollutants, you can ensure optimal equipment performance, maximize efficiency, avoid costly downtime, and contribute to a more sustainable operation. Investing in a turbine oil filter machine is a wise decision that yields long-term benefits for your power generation operations, both financially and environmentally.






