SF6 Gas Filling and Refilling Devices: Essential Equipment for Electrical Maintenance
Electrical equipment used in power transmission and distribution systems often relies on specific gases for insulation and arc quenching. One such gas is sulfur hexafluoride (SF6), known for its excellent insulating properties and ability to extinguish electrical arcs. However, managing SF6 gas throughout a piece of equipment’s lifecycle requires specialized tools. This article explores the functionalities and distinctions between SF6 gas filling devices and refilling devices.
What is SF6 Gas and Where is it Used?
SF6 gas is a colorless, odorless, and nonflammable synthetic gas. Its high dielectric strength, meaning it can withstand high voltage without conducting electricity, makes it ideal for insulating electrical components. Additionally, SF6 gas effectively quenches electrical arcs, which are flashes of electricity that can occur during switching operations in high-voltage systems.
Due to these properties, SF6 gas finds application in various electrical equipment, including:
- Gas-insulated Substations (GIS): These compact substations utilize SF6 gas for insulation instead of air, allowing for a smaller footprint and reduced environmental impact compared to traditional air-insulated substations.
- Circuit Breakers: SF6 gas acts as the insulating and arc quenching medium within circuit breakers, allowing them to safely interrupt electrical current flow when necessary.
- Power Transformers: High-voltage transformers often utilize SF6 gas for insulation due to its superior dielectric strength compared to air, especially for applications requiring compact designs.
The Critical Need for SF6 Gas Filling and Refilling
While SF6 gas offers significant advantages in electrical equipment, maintaining its precise level within the equipment is absolutely necessary for both optimal performance and safety reasons. Here’s a breakdown of why regular SF6 gas filling and refilling procedures are crucial:
1. Addressing SF6 Gas Pressure Loss:
Several factors can lead to a reduction in the pressure of SF6 gas within electrical equipment over time. These factors necessitate the use of refilling devices to maintain the proper gas level.
- Leakage: Even small leaks in seals, valves, or gaskets of the equipment can cause a gradual loss of SF6 gas. These leaks may not be readily apparent, but they can significantly deplete the gas level over time. Regular inspections and leak detection procedures are essential to identify and address any leaks promptly.
- Maintenance Activities: During scheduled maintenance or repair work on equipment containing SF6 gas, the gas may need to be entirely removed for safety reasons. Once the maintenance is complete, refilling the equipment with fresh SF6 gas and restoring the pressure to the manufacturer’s specifications is crucial.
- Degasification: In some instances, a minor phenomenon called degasification can occur during regular equipment operation. Degasification refers to the release of gas molecules from the insulating material within the equipment. While typically minimal, degasification can contribute to a slight decrease in SF6 gas pressure over extended periods.
2. Maintaining Optimal Performance and Safety
The proper level of SF6 gas pressure is critical for ensuring the safe and reliable operation of electrical equipment. Here’s how:
- Electrical Insulation: SF6 gas acts as a superior insulator, preventing electrical current from flowing unintentionally between different components within the equipment. Maintaining the correct gas pressure ensures adequate insulation and prevents electrical arcing (uncontrolled discharges) that can damage the equipment and potentially cause power outages.
- Arc Quenching: In the event of an electrical fault within the equipment, SF6 gas plays a vital role in extinguishing the arc quickly and safely. A sufficient gas pressure level ensures effective arc quenching and minimizes the risk of equipment damage or personnel injury.
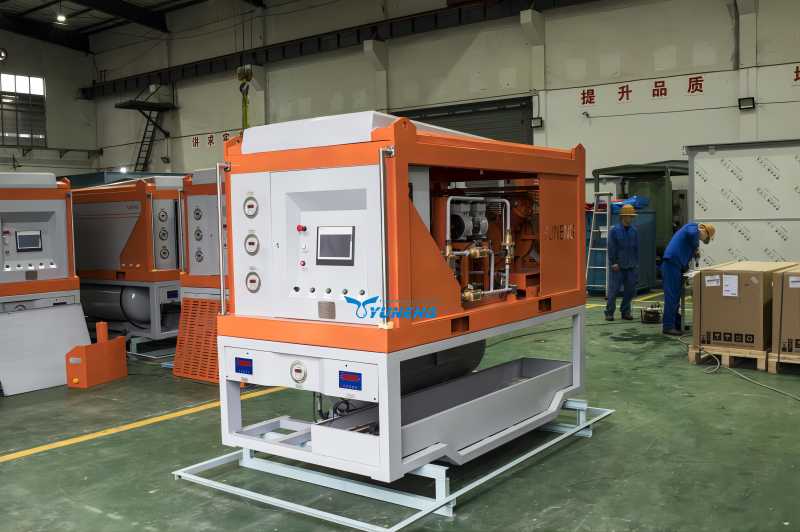

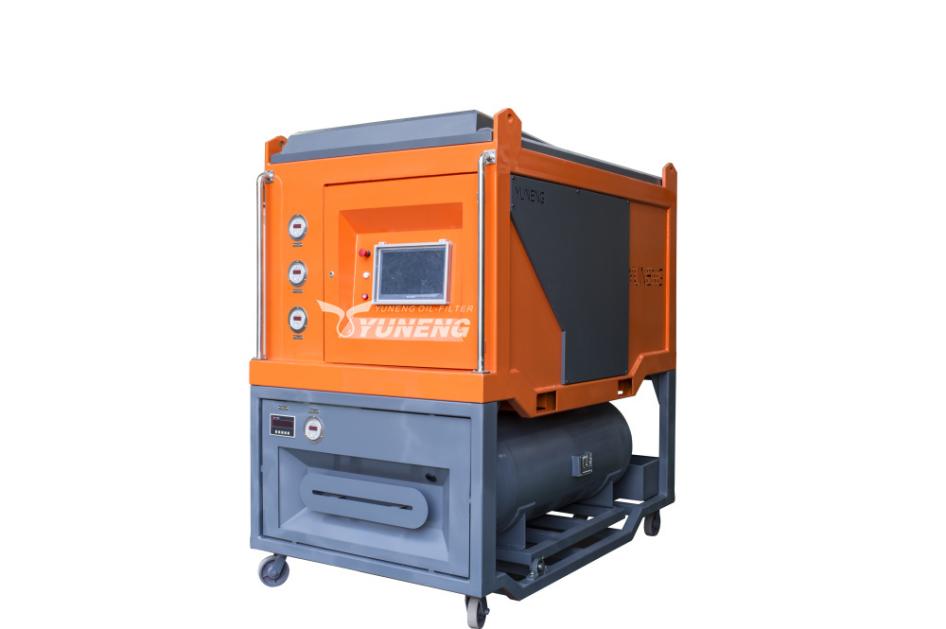
SF6 Gas Filling Devices: Initial Charge for New Equipment
SF6 gas filling devices are specifically designed to introduce a precise amount of fresh SF6 gas into brand new electrical equipment during various stages of its operational journey.
1. Manufacturing Stage
During the manufacturing process of equipment like circuit breakers and transformers, SF6 gas filling devices are utilized to fill the internal compartments with the exact amount of gas specified by the manufacturer’s design. This ensures that upon installation, the equipment has the proper level of SF6 gas to provide optimal electrical insulation and arc quenching capabilities.
2. Installation Stage
Once manufactured, the equipment is transported to its designated location for installation. During this transport process, even minor leaks may occur. To address this possibility, SF6 gas filling devices can be used at the installation site to:
- Top-off the gas level: If any minor leakage occurs during transportation, the filling device can precisely add the required amount of SF6 gas to bring the pressure level up to the manufacturer’s specifications.
- Adjust for specific pressure requirements: In some cases, the installation site may have specific environmental factors (such as high altitude) that necessitate a slightly different SF6 gas pressure level compared to the standard factory fill. The filling device allows for precise adjustment of the gas pressure to meet these specific requirements.
3. Commissioning Stage
Before putting the newly installed equipment into operation, a final stage called commissioning takes place. This stage involves a series of tests and verifications to ensure the equipment is functioning correctly and safely. SF6 gas filling devices often play a role in this stage by:
- Verifying gas pressure: The filling device can be used to measure the existing SF6 gas pressure within the equipment. This ensures the pressure level meets the manufacturer’s specifications and adheres to relevant industry regulations for safe operation.
- Adjusting gas pressure (if needed): If the gas pressure is outside the acceptable range during commissioning, the filling device allows for precise adjustments to bring the pressure to the correct level.
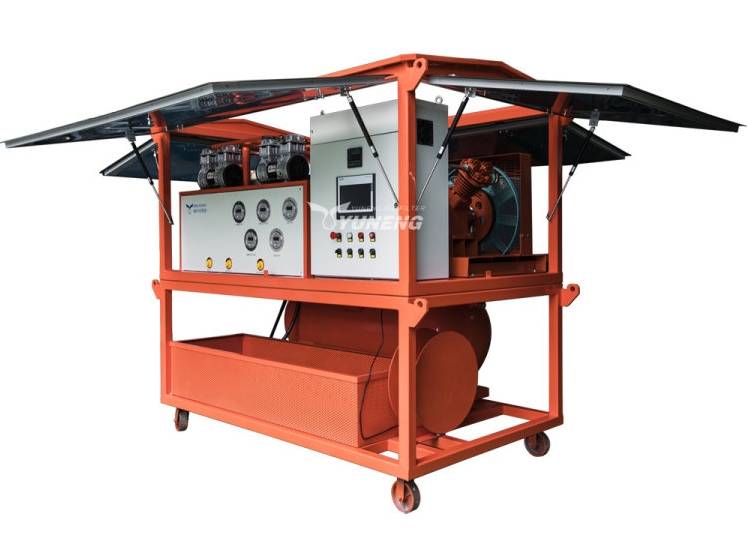

SF6 Gas Refilling Devices: Maintaining Gas Levels in Existing Equipment
Unlike filling devices used for new equipment, SF6 gas refilling devices serve a distinct purpose: maintaining the appropriate pressure level of SF6 gas within existing electrical equipment over its operational lifetime. Here’s a closer look at the factors that necessitate refilling and how these devices address them:
1. Combating Pressure Loss from Leaks
While SF6 gas boasts excellent insulating properties, it’s not entirely immune to leakage. Over extended periods, even minor leaks can develop through various points in the equipment, including:
- Seals: Seals are critical components that create a tight barrier between different compartments within the equipment. Over time, due to factors like wear and tear or exposure to environmental conditions, seals can deteriorate, allowing for small amounts of SF6 gas to escape.
- Valves: Valves are used to control the flow of SF6 gas during maintenance procedures or equipment operation. Similar to seals, valves can develop leaks if they are not properly maintained or if their gaskets become damaged.
- Gaskets: Gaskets are sealing materials used to create a tight fit between different components within the equipment. Like seals, gaskets can also degrade over time, potentially leading to SF6 gas leaks.
These leaks, even if minor, can gradually deplete the overall SF6 gas pressure within the equipment. Regular inspections and leak detection procedures are crucial for identifying and promptly addressing any leaks to minimize SF6 gas loss.
2. Replenishing Gas After Maintenance
During scheduled maintenance or repair work on equipment containing SF6 gas, the gas may need to be entirely removed for safety reasons. This removal process is often necessary to ensure the safety of personnel working on the equipment and to prevent potential electrical hazards.
Once the maintenance activities are complete, SF6 gas refilling devices become essential. These devices allow technicians to:
- Reintroduce fresh SF6 gas: After maintenance, the equipment requires a refill of fresh SF6 gas to restore its insulating and arc quenching capabilities. Refilling devices enable the safe and controlled introduction of the required amount of gas.
- Restore pressure to the specified level: Each piece of equipment has a manufacturer-defined optimal pressure level for the SF6 gas. Refilling devices are equipped with pressure gauges and control mechanisms that allow technicians to precisely adjust the gas pressure within the equipment to meet these specifications.

Distinguishing Between Filling and Refilling Devices:
While both filling and refilling devices handle SF6 gas transfer, a key distinction lies in their primary application, here is a summary table as follows:
| Feature | SF6 Gas Filling Device | SF6 Gas Refilling Device |
| Primary Application | Introduce fresh SF6 gas into new equipment | Replenish SF6 gas in existing equipment |
| Typical Use Cases | 1. Manufacturing of equipment (circuit breakers, transformers) 2. Top-off during installation (addressing minor leaks or adjusting for pressure requirements) 3. Commissioning (verifying and adjusting gas pressure) | 1. Addressing pressure loss due to leaks in seals, valves, or gaskets 2. Refilling after maintenance procedures (reintroducing gas and restoring pressure) |
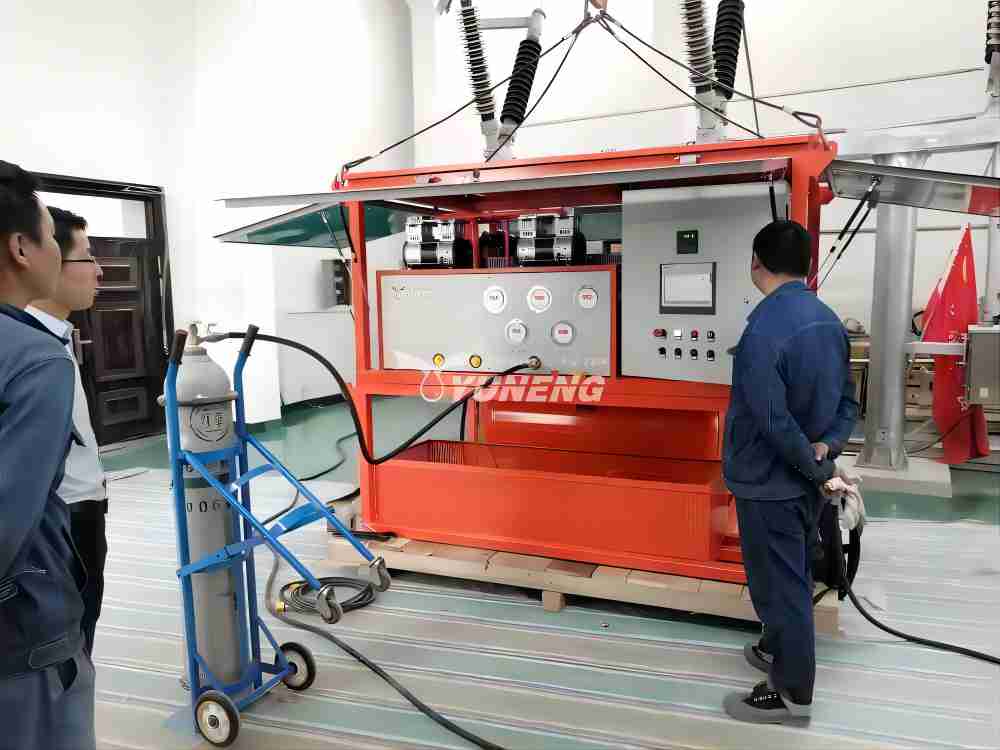
Features of SF6 Gas Filling and Refilling Devices: Ensuring Safe and Precise Gas Transfer
Modern SF6 gas filling and refilling devices incorporate several key features to guarantee safe, efficient, and controlled transfer of the gas. Here’s a detailed breakdown of these features:
1. Pressure Gauges
These gauges are essential instruments that display real-time pressure readings in two critical locations:
- Source Cylinder Pressure: One gauge measures the pressure of the SF6 gas within the source cylinder from which the gas is being transferred. This information allows technicians to monitor the remaining gas quantity in the cylinder and ensure sufficient gas is available for the filling or refilling operation.
- Equipment Pressure: The other gauge displays the pressure of the SF6 gas within the equipment being filled or refilled. By monitoring this pressure in real time, technicians can precisely control the gas flow and ensure the equipment reaches the desired pressure level without exceeding it.
2. Shutoff Valves
These valves act as control points for the SF6 gas flow during the filling or refilling process. They are typically manual valves operated by technicians and offer precise control over gas transfer.
- Opening and Closing: Technicians can open and close the shutoff valves at specific points in the process to:
- Initiate gas flow from the source cylinder to the equipment.
- Regulate the gas flow rate to achieve a gradual and controlled pressure increase within the equipment.
- Stop the gas flow entirely when the desired pressure level is reached or in case of any unforeseen circumstances.
- Preventing Accidental Overfilling: By controlling the gas flow through shutoff valves, technicians can prevent accidental overfilling of the equipment. Overfilling can damage equipment components and pose safety risks.
3. Self-Closing Couplings
These specialized connectors establish a secure and leak-proof connection between the SF6 gas filling/refilling device and the equipment being serviced. They offer several advantages:
- Secure Connection: Self-closing couplings ensure a tight and reliable connection, minimizing the risk of gas leaks during the transfer process.
- Automatic Closure: When disconnected from the equipment, these couplings automatically close, preventing any accidental release of SF6 gas after the connection is broken. This feature is crucial for minimizing environmental impact and ensuring personnel safety.

Importance of Responsible SF6 Gas Management
While SF6 gas offers significant benefits in electrical equipment, its potent greenhouse gas properties necessitate responsible handling throughout its lifecycle. Here’s a breakdown of key aspects for minimizing environmental impact:
1. Minimizing Leaks
- Impact of Leaks: Leaks of SF6 gas from electrical equipment can significantly contribute to climate change. SF6 has a global warming potential thousands of times greater than carbon dioxide (CO2). Even minor leaks can accumulate over time, leading to a substantial environmental impact.
- Leak Prevention Strategies: Several practices are crucial to minimize leaks:
- Equipment Maintenance: Regularly scheduled maintenance of electrical equipment containing SF6 gas helps identify and address potential leak points before they occur. This includes inspecting seals, valves, and gaskets for signs of wear or damage.
- Leak Detection Equipment: Utilizing specialized leak detection equipment allows technicians to pinpoint even minor leaks precisely. Early detection and repair of leaks significantly reduce SF6 gas emissions.
- Prompt Leak Repair: Once a leak is detected, it’s essential to repair it promptly to minimize further SF6 gas loss and its environmental consequences.
2. SF6 Gas Recycling and Reclamation
- Beyond Venting: Traditionally, used SF6 gas was often vented into the atmosphere after equipment servicing. However, responsible practices advocate for capturing and recycling the gas.
- Recycling Process: Specialized recycling facilities can remove impurities and contaminants from used SF6 gas. This reclaimed SF6 can then be reused in electrical equipment, reducing the need for virgin gas production and minimizing the environmental footprint associated with SF6 gas usage.
3. Regulations and Reporting
- Regulatory Framework: Many countries and regions have implemented regulations governing the use, handling, and disposal of SF6 gas. These regulations aim to ensure the safe and environmentally responsible management of this potent greenhouse gas.
- Key Regulatory Aspects: Regulations typically cover aspects like:
- Emission Reporting: Facilities utilizing or handling SF6 gas may be required to report their SF6 gas emissions to relevant authorities. This data collection helps track overall SF6 gas usage and identify areas for improvement.
- Certified Personnel: Regulations often mandate that only certified personnel with specialized training handle SF6 gas during filling, refilling, and equipment maintenance procedures. This ensures proper handling techniques are followed to minimize leaks and environmental impact.

Conclusion
SF6 gas filling and refilling devices play a vital role in maintaining the functionality and safety of electrical equipment. However, responsible management of SF6 gas is paramount throughout its lifecycle due to its potent greenhouse gas nature.
As research and development continue in the field of alternative insulating mediums, the reliance on SF6 gas may gradually decrease. However, in the foreseeable future, SF6 gas will likely remain a crucial component in electrical grids. By adopting a comprehensive approach that prioritizes responsible use, leak mitigation, and gas recycling, we can ensure the continued safe and reliable operation of our electrical infrastructure while minimizing the environmental impact of SF6 gas. The future of electrical insulation lies in striking a sustainable balance between technological advancements and environmental responsibility.
