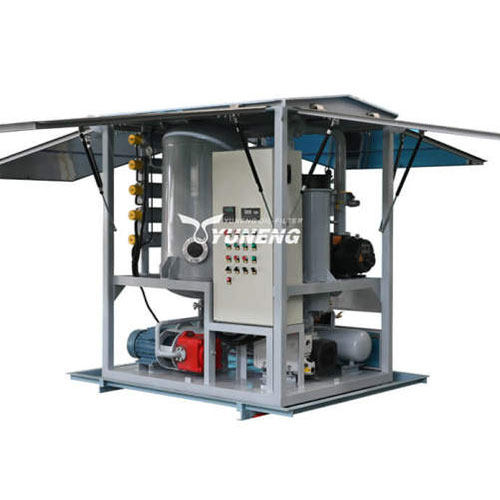
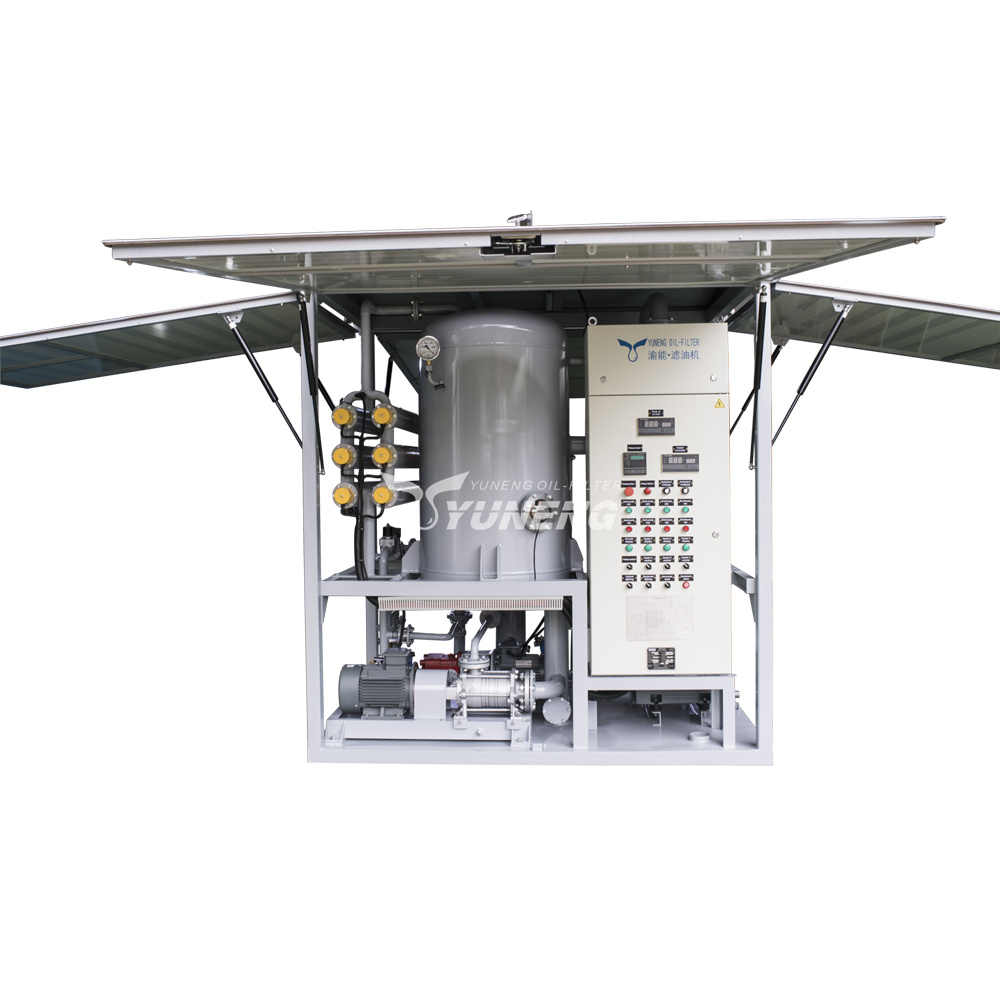
How Often Should You Regenerate Transformer Oil? Best Practices
Table of Contents
Transformer oil is essential in providing insulation and cooling to power transformers, but over time, its performance degrades due to chemical and environmental influences. Regeneration offers an economical alternative to replacement; so, when should I regenerate transformer oil?
Why Transformer Oil Degrades?

Transformer oil plays an essential role in providing insulation and cooling, yet over time, its condition deteriorates due to various factors:
- Oxidation– When exposed to oxygen, oil reacts chemically with atmospheric air molecules to produce sludge, acids, and other byproducts that diminish its insulation properties and decrease dielectric strength, and speed up aging processes.
- Moisture Contamination– When moisture from leakage, humidity, or condensation enters, dielectric strength decreases significantly while speeding aging processes forward significantly.
- Thermal Stress – Operating temperatures that break down oil’s chemical structure accelerate its degradation, leading to faster degradation.
- Electrical Stress – Arcing and partial discharges generate gases and carbon particles, which pollute the oil supply, thus polluting its purity.
- Particulate Contamination – Dust, metal particles, and insulation fibers may accumulate and impair performance, ultimately decreasing oil viscosity and oxidation stability over time due to natural wear-and-tear processes.
- Chemical Breakdown – Over time, natural wear-and-tear has the effect of gradually making oil less viscous over time and leading to its chemical breakdown, eventually rendering its performance unreliable for use.
Degraded oil can quickly lead to overheating, insulation failure, and costly transformer damage if left unchecked. Regular testing and timely regeneration help maintain optimal performance while prolonging its lifespan.
Key Factors Determining Transformer Oil Regeneration Frequency

Several critical factors influence how often transformer oil needs regeneration. Understanding these variables helps optimize maintenance schedules and prevent unexpected failures.
Oil Condition Monitoring Results
Regular oil testing provides the most reliable indication of regeneration needs:
- Acidity (TAN): Renew when acidity (TAN) exceeds 0.1 mg KOH/g.
- Dielectric Strength: If breakdown voltage drops below 30kV, intervention is required immediately.
- Moisture Content: Critical Threshold of 30 PPM for most Transformers (higher for older transformers).
- Dissolved Gas Analysis (DGA): Sudden increases in dissolvable gases can indicate thermal/electrical faults that have recently arisen.
- Interfacial Tension: Values below 25 dynes/cm may indicate that there may be an accumulation of oxidation products.
Transformer Operating Parameters
- Load Cycling: Constant load fluctuations have an adverse impact on oil aging.
- Temperature Exposure: Working above 65degC doubles oxidation rate.
- Overload Conditions: Transformers operating at more than 110% capacity need more frequent checks to detect overload conditions.
Environmental & Design Factors
| Factor | Impact on Regeneration Frequency |
| Sealed vs. Free-breathing | Free-breathing designs require 2-3× more frequent maintenance |
| Indoor vs. Outdoor | Outdoor units need 30-50% shorter intervals due to weather exposure |
| Coastal/Industrial Areas | Salt, pollution may cut intervals by half compared to clean environments |
| Age of Equipment | Transformers >15 years often need 25% more frequent oil treatment |

Historical Maintenance Data
- Compare oil degradation rates of previous regeneration cycles
- Compare with manufacturer’s anticipated lifespan for your specific oil type.
- Note any correlations between electrical faults and oil condition.
Pro Tip: Implementing condition-based maintenance rather than fixed schedules allows for optimal timing of regeneration while avoiding unnecessary servicing.
How Often Should You Regenerate Transformer Oil?
| Condition | Recommended Action |
| Annual testing shows minor contamination | Filter & purify (no full regeneration yet) |
| Moderate oxidation (TAN 0.1–0.5 mg KOH/g) | Regenerate every 3–5 years |
| Severe contamination (TAN > 0.5, high moisture, low BDV) | Immediate regeneration |
| Transformers in harsh environments | Check every 1–2 years, regenerate as needed |
Transformer oil regeneration frequency isn’t a one-size-fits-all schedule—it depends on your equipment’s condition, operating environment, and performance data. However, industry best practices provide clear guidelines to help optimize maintenance intervals.
Signs You Need Oil Regeneration Sooner:
Increased transformer noise or overheating
Dark, cloudy oil with sludge
Rising levels of furans (an indicator of paper insulation degradation)
Best Practices for Transformer Oil Regeneration Machines
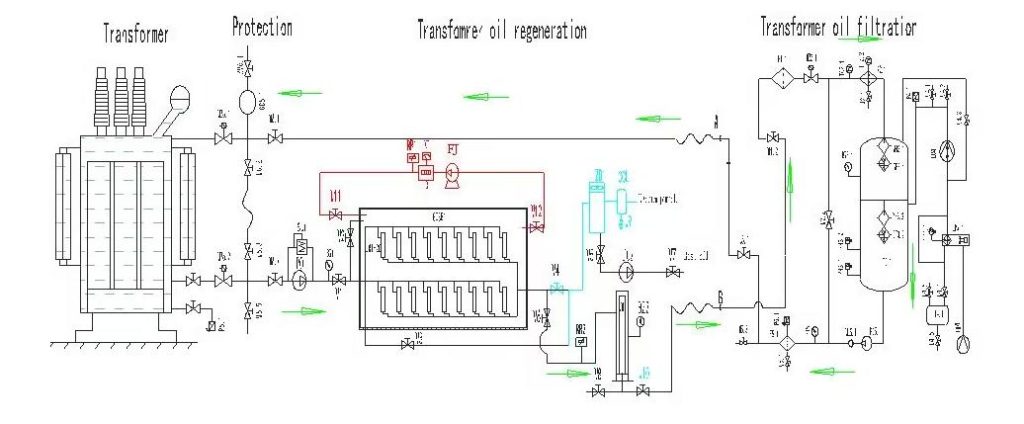
To maximize the efficiency of regeneration of transformer oil and prolong the life of equipment , be sure to follow these important operating guidelines:
1. Pre-Treatment Preparation
Always begin with a thorough oil test to determine the contamination levels. This helps you choose the right regeneration technique, whether it is simple filtration, dehydration, or complete chemical restoration. Get rid of large particles by pre-filtration to avoid clogging of the regeneration process.
2. Optimal System Selection
Select equipment that is compatible with the volume of your oil and the type of contamination:
- Mobile units to provide on-site maintenance of big transformers
- Vacuum dehydration systems for moisture removal
- Adsorbent clay towers for extreme oxygenation cases
Check that the flow rate and temperature control match your oil specifications.
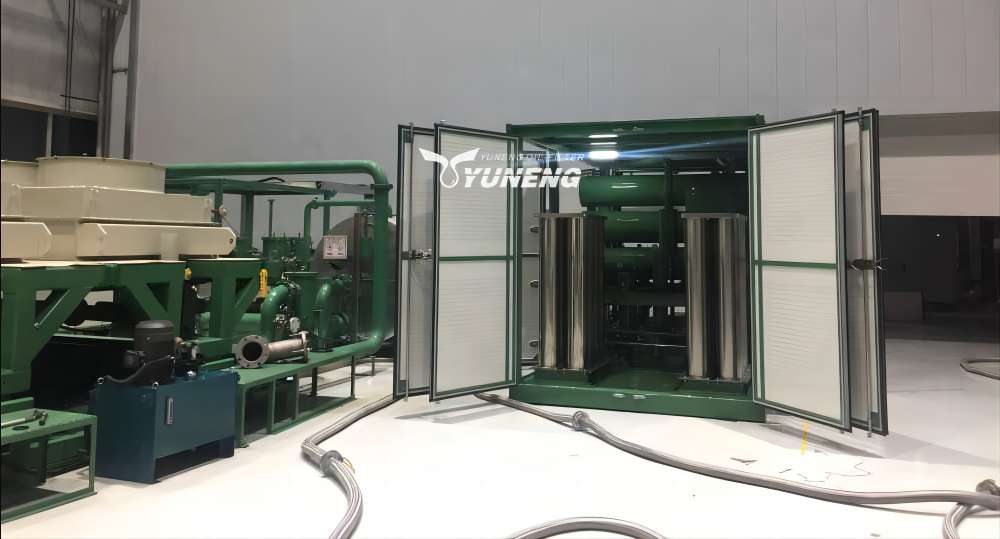

3. Controlled Processing Parameters
Maintain precise operating conditions during regeneration:
- Keep the oil temperature between 50 and 65 °C to prevent thermal degradation
- Set the vacuum levels according to the amount of moisture (typically 0.1-1 Mbar)
- Check the quality of processed oil in real-time using dielectric strength testers
4. Post-Regeneration Validation
Never allow oil to be returned to service without testing verification. Confirm key parameters–including acidity, dielectric strength, and moisture levels–meet IEEE or IEC standards. Record all results to maintain records and for trend analysis.
5. Preventive Maintenance of Equipment
- Replace the filter elements and adsorbent material after every cycle of regeneration
- Check the calibration of gauges and sensors annually.
- Cleanse system lines to avoid cross-contamination between work environments
Following these guidelines, operators can achieve the highest oil recovery rates while reducing downtime for transformers. Regular regeneration not only improves oil performance, but it can also triple the time between oil changes.
For more information about Transformer Oil Regeneration Machines, please feel free to reach us!






