Step-by-Step Guide to Safe SF6 Gas Handling and Post-Work Practices
SF6 gas (sulfur hexafluoride) is a widely used electrical insulator in high voltage equipment. While offering excellent insulating properties, SF6 gas presents unique safety considerations due to its weight, asphyxiating nature, and environmental impact. This article outlines the critical procedures for safe and responsible handling of SF6 gas.
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) and Pre-work Considerations
SF6 gas, while crucial for electrical insulation, poses unique safety challenges. Fortunately, a robust Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) ensemble acts as your first line of defense. Here’s a detailed breakdown of the essential PPE for SF6 gas handling:
- Safety Glasses (ANSI Z87.1 approved): Your eyes are vulnerable to accidental splashes or debris during transfers or equipment malfunctions. Choose safety glasses that comply with the American National Standards Institute (ANSI) Z87.1 standard for occupational eye and face protection. Consider anti-fogging lenses to maintain clear vision in humid environments.
- Chemical-resistant Gloves (butyl rubber, Viton®, Barricade®): SF6 gas can irritate or harm the skin upon contact. Select gloves crafted from materials like butyl rubber, Viton®, or Barricade® – known for their exceptional resistance to SF6. Double gloving provides an extra layer of protection in case of a tear or puncture in the outer glove. Regularly inspect your gloves for signs of damage and replace them promptly to maintain their effectiveness.
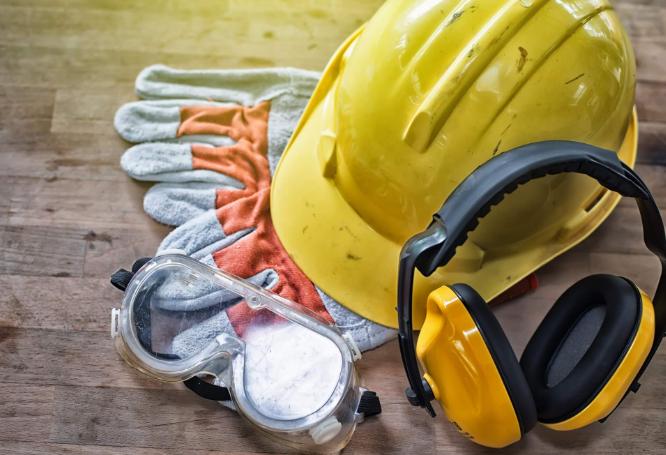

- Safety Boots: Sturdy safety boots with good traction are essential to prevent slips and falls, especially when working on wet or uneven surfaces. Consider steel-toed boots for additional protection against falling objects.
- Respirator (approved for non-oxygen-deficient environments): SF6 gas displaces oxygen, posing an asphyxiation risk. Utilize a respirator specifically approved for non-oxygen-deficient environments. Ensure the respirator has appropriate filters designed to capture SF6 gas particles. Proper fit testing is crucial to guarantee a secure seal and optimal protection.
- Hearing Protection: Working near noisy equipment like compressors or gas transfer pumps can damage your hearing. Invest in earplugs or earmuffs with a Noise Reduction Rating (NRR) suitable for the noise level in your work area.
Pre-work Considerations: Preparing a Safe Stage for SF6 Gas Handling
Before embarking on any SF6 gas handling activity, meticulous preparation is paramount. Here are key pre-work considerations to ensure a safe and controlled environment:
- Mandatory Training: Ensure all personnel involved in SF6 gas handling undergo comprehensive training. This training should encompass the physical and chemical properties of SF6 gas, the associated hazards, safe handling procedures, leak detection methods, emergency response protocols, and relevant local regulations governing SF6 gas handling and disposal.
- Work Permit (if required): Depending on your location and the specific nature of the work, obtaining a work permit from the relevant authorities might be mandatory. Familiarize yourself with the permit requirements in your area and secure the necessary permits before commencing any SF6 gas handling activities.
- Well-ventilated Workspace: SF6 gas is heavier than air and can displace oxygen in poorly ventilated spaces. Choose a well-ventilated workspace with open doors and windows whenever possible. If working indoors, ensure adequate ventilation systems are operational throughout the handling process. Confined spaces should be strictly avoided for SF6 gas handling activities.
- Leak Detection Equipment: Proactive leak detection is crucial for minimizing environmental impact and ensuring worker safety. Keep SF6-specific leak detection equipment readily available at the worksite. Common leak detection methods for SF6 gas include corona discharge detectors, ultrasonic detectors, and sniffer devices. Ensure these instruments are properly calibrated for accurate leak identification.
- Emergency Response Plan: Develop and rehearse a comprehensive emergency response plan to address potential scenarios like accidental inhalation, leaks, or equipment failure. The plan should outline first-aid procedures, evacuation protocols, and emergency contact information. By familiarizing yourself and your team with the emergency response plan, you can ensure a coordinated and effective response in the event of an incident.
Following these comprehensive PPE and pre-work considerations equips you with the necessary knowledge and safeguards to handle SF6 gas safely and responsibly. Remember, prioritizing safety and meticulous preparation are the cornerstones of successful and sustainable SF6 gas handling practices.

Preparing the Equipment and Gas Cylinders
Safe and efficient SF6 handling relies heavily on having the right equipment in proper working order and using gas cylinders that are in good condition. Here’s a detailed breakdown of this crucial step:
Equipment Preparation
- Specific Equipment Selection: The specific equipment needed will depend on the task at hand. Here are common examples:
- Filling: Filling units typically include a pressure regulator, hoses, adapters for different equipment types, and a connection for the SF6 gas cylinder. Some advanced units might have built-in leak detectors and gas analysis capabilities.
- Recovery: Recovery units are designed to evacuate and capture SF6 gas from electrical equipment. They usually consist of a compressor, filters, a condenser, and a storage tank for the recovered gas.
- Leak Detection: Electronic leak detectors specifically designed for SF6 gas are essential. These detectors are highly sensitive and can pinpoint even small leaks.
- Pre-use Inspection: Before each use, thoroughly inspect all equipment for damage, leaks, or loose connections. Pay close attention to hoses, gauges, valves, and any electrical components
- Leak Testing: Some equipment, like filling units, might require periodic leak testing to ensure their integrity. Refer to the manufacturer’s recommendations for specific testing procedures.
- Calibration: Pressure gauges and other measuring instruments should be calibrated regularly to ensure accurate readings during SF6 handling.
Gas Cylinder Preparation
- Storage and Handling: SF6 gas cylinders must be stored according to regulations. This typically involves keeping them upright in a cool, dry, and well-ventilated area, out of direct sunlight and away from heat sources.
- Cylinder Inspection: Before using a cylinder, perform a visual inspection for any signs of damage, corrosion, leaks, or loose valves. Do not use damaged cylinders.
- Cylinder Valve Operation: Ensure the cylinder valve cap is securely in place before transporting the cylinder. Only trained personnel should operate the cylinder valve.
- Gas Cylinder Information: Review the information label on the cylinder. This will provide details like the type and quantity of SF6 gas, manufacturing date, and any relevant safety information.
Additional Considerations:
- Manufacturer’s Instructions: Always refer to the manufacturer’s instructions for the specific equipment and gas cylinders being used. These instructions will provide detailed information on proper operation, maintenance, and safety precautions.
- Record Keeping: Maintain records of the equipment used, gas cylinder identification, and the date of the SF6 handling activity.
By following these steps and ensuring proper equipment and gas cylinder preparation, you can significantly reduce the risk of accidents and ensure safe and efficient SF6 handling.

SF6 Gas Handling Procedures
The specific procedures for handling SF6 gas will vary depending on the task at hand. Here’s a detailed breakdown for three common procedures: Filling, Recovery, and Leak Detection:
Filling Procedure
- System Preparation: Before introducing fresh SF6 gas, the equipment must be purged with dry air or nitrogen. This removes any moisture or contaminants that could degrade the SF6’s insulating properties and potentially lead to harmful byproducts.
- Connecting Equipment: Once purging is complete, connect the filling equipment and gas cylinder following the manufacturer’s instructions. Ensure all connections are secure and leak-tight.
- Filling and Monitoring: Open the cylinder valve slowly and begin filling the equipment. Closely monitor the pressure gauges on both the cylinder and the equipment to ensure you stay within the designated pressure range. Never exceed the pressure limits specified for the equipment.
Recovery Procedure
- System Evacuation: The first step is to evacuate the SF6 gas from the equipment. Connect the recovery unit and begin the evacuation process, following the manufacturer’s instructions. Reduce the pressure in the system to a pre-determined level suitable for the recovery unit.
- Gas Transfer: Once the desired vacuum is reached, activate the recovery unit to transfer the recovered SF6 gas into its designated container. The recovered gas should be transferred to a certified reclaimer for proper processing and reuse.
- System Purging (Optional): After complete recovery, consider purging the system again with dry air or nitrogen. This removes any residual SF6 gas and minimizes the risk of emissions.
Leak Detection Procedure
- Leak Detector Selection: Only use an approved SF6 leak detector designed for the specific concentration range you expect to encounter. Different leak detectors have varying sensitivities.
- Following Manufacturer’s Instructions: Carefully follow the manufacturer’s instructions for operating the chosen leak detector. This will ensure proper calibration, operation, and interpretation of results.
- Systematic Inspection: Systematically scan the equipment for leaks, paying close attention to valves, flanges, and other connection points. The leak detector will provide an audible or visual alert if it detects SF6 gas above the pre-set threshold.
Remember, these are general guidelines. Always refer to the specific equipment manufacturer’s instructions and relevant regulations for detailed procedures and safety precautions.
Post-work Procedures and Safe SF6 Gas Handling Practices
Once the SF6 gas handling task is complete, following proper post-work procedures is crucial to ensure safety and environmental responsibility. Here’s a detailed breakdown of these essential steps:
- Secure the System: Double-check that all valves on the equipment and gas cylinders are properly closed. This prevents accidental releases and ensures the system is isolated. Disconnect any hoses or transfer lines used during the process. Cap all open connections on the equipment and hoses to prevent contamination or moisture ingress.
- Leak Detection Verification: After completing a filling procedure, it’s advisable to perform a final leak check using an approved SF6 leak detector. This verifies the integrity of the system and ensures a successful filling operation. If a leak is identified, isolate the area, evacuate any remaining SF6 gas safely, and refer to qualified personnel for repair before restarting the equipment.
- Disposal of Contaminated Materials: During the handling process, there’s a possibility of minor spills or drips. Any rags or wipes used to clean up spills should be collected in a sealed container designated for hazardous waste disposal. Consult your local regulations for proper disposal procedures for SF6-contaminated materials.
- Equipment Decontamination: If the equipment itself becomes contaminated with SF6, it should be decontaminated by qualified personnel following established procedures. This might involve purging the system with dry air or nitrogen to remove residual gas.
- Record Keeping: Maintaining accurate records is essential for tracking SF6 gas usage and ensuring compliance with regulations. Document the date, type of work performed (filling, recovery, leak detection), quantity of SF6 gas used or recovered, and any relevant observations or issues encountered.
By following these post-work procedures and safe handling practices, you can minimize the environmental impact of SF6 gas and ensure the safety of yourself and others in the workplace. Remember, if you are unsure about any aspect of the SF6 handling process, always seek guidance from a qualified supervisor or professional.

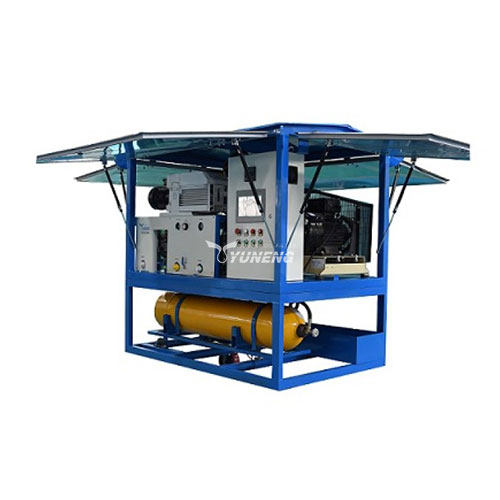
YUNENG SF6 Gas Handling Plants
YUNENG is a manufacturer with rich experience in the production of SF6 gas handling equipment.
These plants are designed to provide a comprehensive and environmentally responsible approach to handling SF6 gas during various industrial applications. Here’s a breakdown of how YUNENG’s SF6 gas handling plants can be integrated into your SF6 gas management strategy:
- SF6 Gas Recovery and Refilling: YUNENG’s plants are equipped to recover SF6 gas from electrical equipment undergoing maintenance or decommissioning. This recovered gas undergoes a purification process within the plant, removing contaminants and moisture. The purified gas can then be refilled into cylinders for reuse, minimizing waste and maximizing resource efficiency.
- Environmentally Friendly Operation: YUNENG’s plants prioritize environmental responsibility. Their systems capture over 99.9% of recovered SF6 gas, preventing its release into the atmosphere. This significantly reduces the environmental impact associated with SF6 gas usage.
- Efficiency and Ease of Use: YUNENG’s SF6 gas handling plants are designed for user-friendliness and operational efficiency. The plants are equipped with automated controls and user-friendly interfaces, simplifying the SF6 gas recovery and refilling process.
- Applications: These plants cater to various industries that utilize SF6 gas, including:
- Power transmission and distribution companies
- Electrical equipment manufacturers and maintenance providers
- Renewable energy facilities (wind farms, solar plants)
If you are in any needs of our products, please feel free to contact us.
