Why and How to Perform a BDV Test on Transformer Oil with an Oil Tester
Testing the insulation oil breakdown voltage (BDV) is an important method for evaluating the dielectric strength and quality of transformer oil or other insulating oils. The Oil BDV Tester is a specialized device designed for this purpose.
Table of Contents
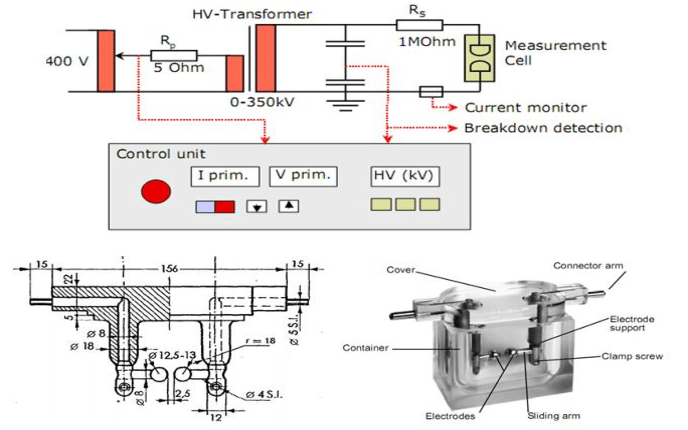
Basics of Breakdown Voltage of Transformer Oil
When we talk about the health and reliability of transformer oil, one of the most fundamental parameters to examine is its Breakdown Voltage. To help you clearly understand this concept, let’s explore the basics step by step — including what BDV means, why it matters, how it is measured, the factors that affect it, and the standard values recognized by the industry.
What Does Breakdown Voltage Mean
The Breakdown Voltage (BDV) is the lowest voltage at which an insulating material begins to lose its ability to resist electrical current, allowing it to conduct electricity. For transformer oil, the BDV represents the voltage at which the oil ceases to be an effective insulator and arcing forms between the electrodes. This value reflects the dielectric strength of the oil and is a key indicator of its ability to protect the transformer’s internal components from electrical stresses.
Why Is BDV Important in Transformer Oil
The Breakdown Voltage of transformer oil directly measures the oil’s insulating properties and its ability to protect the transformer from electrical faults. Oil with a high breakdown voltage effectively protects the transformer’s internal components from arcing and voltage surges, maintaining safe and reliable operation.
On the other hand, a low breakdown voltage may indicate the presence of moisture, impurities, or gases in the oil, which can compromise insulation properties and increase the risk of equipment failure or costly power outages. Therefore, regular breakdown voltage testing is crucial to monitoring oil condition, preventing failures, and extending transformer life.
How Is the BDV of Transformer Oil Measured
BDV testing involves placing oil between two electrodes set at a fixed gap (commonly 2.5 mm as per IEC 60156). A gradually increasing AC voltage is applied until the oil breaks down and an electric arc occurs. The voltage at this point is recorded as the BDV value.
| BDV Range | Oil Condition | Implications |
| High (>60 kV) | Excellent | Oil is clean, dry, and provides strong insulation. |
| Acceptable (30–60 kV) | Usable | Oil is still functional but should be monitored regularly. |
| Low (<30 kV) | Contaminated or aged | Oil may contain moisture or impurities; requires treatment or replacement to avoid transformer failure. |
5 Key Factors That Reduce Transformer Oil BDV
- Moisture Content: The presence of moisture in the oil significantly reduces its BDV by forming conductive pathways.
- Contaminant Intrusion: Dust, dirt, and metal particles compromise oil purity and decrease its ability to resist breakdown.
- Aging and Oxidation: Over time, inherent aging and oxidation processes naturally weaken the oil’s insulating strength.
- Dissolved Gas Analysis: During aging and stress, the oil releases signature gases like hydrogen and carbon dioxide. Combining BDV testing with dissolved gas analysis provides valuable insights into potential transformer faults for early detection and corrective action.
- Operational Stress and Thermal Management: High operating temperatures, overloading, and arcing events accelerate oil degradation and negatively impact BDV.

Industry Standards for BDV Values
According to the International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC 60156), transformer oil should have a BDV not less than 30 kV to be considered safe. Fresh transformer oil typically shows BDV values above 60 kV, while oil in service may test lower depending on age and operating conditions.
Step-by-Step Procedure to Test Oil BDV
Testing the Breakdown Voltage of transformer oil is essential for assessing its insulating performance and ensuring transformer safety. Here’s a detailed step-by-step guide on how to perform this test using an Oil BDV Tester.
Preparation
Before testing, carefully prepare the oil sample. Collect the oil sample in a clean, dry, and airtight container, avoiding any moisture, dust, or air bubbles, as these can reduce the transformer oil’s Breakdown Voltage.
Next, thoroughly clean the test cell (whether glass or acrylic) and electrodes. Make sure to completely dry them to prevent any contamination that could affect measurement accuracy.
Finally, set the electrode gap according to standard testing procedures. A typical gap, as specified in IEC 60156 or ASTM D1816, is 2.5 mm. Adjust the gap according to your specific testing standard to ensure accurate results.
Filling the Test Cell
When filling the test cell, pour the oil sample slowly to prevent air bubbles from being trapped, which could affect the accuracy of the BDV measurement. Make sure the electrodes are fully submerged in the oil to ensure proper testing conditions. If any bubbles appear on the surface, gently stir them with a clean glass rod or allow them to disperse naturally before proceeding.
Setting up the Oil BDV Tester
After filling the test cell, carefully insert it into the BDV tester chamber. Make sure the protective cover is closed, as modern testers are equipped with safety interlocks to prevent exposure to high voltage. Next, set the testing parameters according to the relevant standards (IEC, ASTM, IS), including the voltage rise rate, number of tests, electrode type, and gap distance, to ensure accurate and consistent results.
Performing the Test
To begin, start the test by allowing the tester to apply a gradually increasing AC voltage, typically at a rate of 2 kV/s. Carefully monitor for breakdown, which occurs when the oil can no longer insulate and an electric arc forms, indicating the BDV has been reached. Modern testers feature an automatic trip function that shuts off immediately to protect both the equipment and the operator. Finally, record the BDV, which is displayed digitally or on the tester’s meter for accurate documentation.
Repetition and Averaging
After completing the initial test, empty the test cell and gently stir the remaining oil to ensure it is homogenized. Then, repeat the test using fresh portions of the same oil sample, typically performing 5–6 tests to ensure reliability. Finally, calculate the average BDV by taking the mean of all readings, which serves as the final breakdown voltage value for the sample.
Typical Standards
| Standard | Electrode Gap | Electrode Type | Voltage Rise Rate |
| IEC 60156 | 2.5 mm | Spherical | 2 kV/s |
| ASTM D1816 | 0.5–1 mm | Spherical | Standard varies |
| IS 6792 | 2.5 mm | Spherical | Similar to IEC |
Acceptance Criteria
| Oil Condition | BDV Value | Action / Notes |
| New Oil | > 60 kV | Suitable for use |
| In-Service Oil | < 30 kV | Likely contaminated or aged; requires filtration or replacement |
Regular BDV testing helps detect moisture, contamination, or aging early, protecting transformers from electrical failures and extending their operational life.
Why Should a BDV Test Be Performed on the Insulating Oil of The Transformer?
Regular breakdown voltage (BDV) testing of the insulating oil in transformers acts as a crucial diagnostic tool, providing insights into the oil’s health and insulating ability, ultimately safeguarding the transformer from potentially catastrophic failures. Here’s a breakdown of why BDV testing is essential:
Ensuring Safety
- Early Detection of Deterioration: Transformer oil naturally degrades over time due to factors like moisture, contamination, and oxidation. BDV testing detects these changes before they compromise the oil’s insulating properties, preventing potential breakdowns and arcing faults, which can damage the transformer and pose safety risks to personnel and equipment.
- Proactive Maintenance: By identifying changes in BDV early, maintenance teams can implement timely corrective actions like filtration or oil replacement, preventing further deterioration and costly repairs.
- Regulatory Compliance: Many regions have regulations mandating periodic BDV testing of transformer oil. Complying with these regulations not only ensures safety but also avoids potential legal ramifications.
Optimizing Performance
- Maximized Lifespan: Regular BDV testing helps ensure the oil functions optimally, extending the transformer’s lifespan and saving on replacement costs.
- Improved Reliability: Timely oil maintenance based on BDV results minimizes the risk of unexpected outages, ensuring a more reliable and stable power supply.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Early detection and correction of oil issues through BDV testing prevents more significant and expensive problems down the line, making it a cost-effective maintenance practice.
Additionally, BDV testing is a relatively simple and non-invasive procedure, ensuring minimal downtime for transformer operations. It is user-friendly and portable, allowing for on-site testing, further enhancing convenience.
The Principle of Insulating Oil BDV Test
The principle behind insulating oil Breakdown Voltage (BDV) testing involves placing a sample of the insulating oil into an oil cup, followed by the addition of a controlled rate of voltage increase. The voltage is steadily raised until either the insulating oil breaks down or the applied voltage reaches the maximum test voltage value. This process yields the dielectric strength of the insulating oil, crucial for assessing its suitability for use in transformers and other electrical equipment.
However, achieving accurate results in BDV testing is influenced by various factors, including the distribution of impurities within the insulating oil. Impurities can disperse unevenly due to factors such as Brownian motion, which describes the random movement of particles suspended in a fluid. As a result, the test results for breakdown voltage may exhibit dispersion, necessitating multiple tests to obtain reliable data.
Given the stringent conditions required for oil breakdown voltage testing, specialized equipment known as breakdown voltage testers are employed. These testers are designed to meet the precise requirements of the testing process, ensuring accurate and repeatable results. By conducting BDV testing under controlled conditions, manufacturers and operators can assess the quality and performance of insulating oils with confidence, thereby maintaining the integrity and reliability of electrical systems.
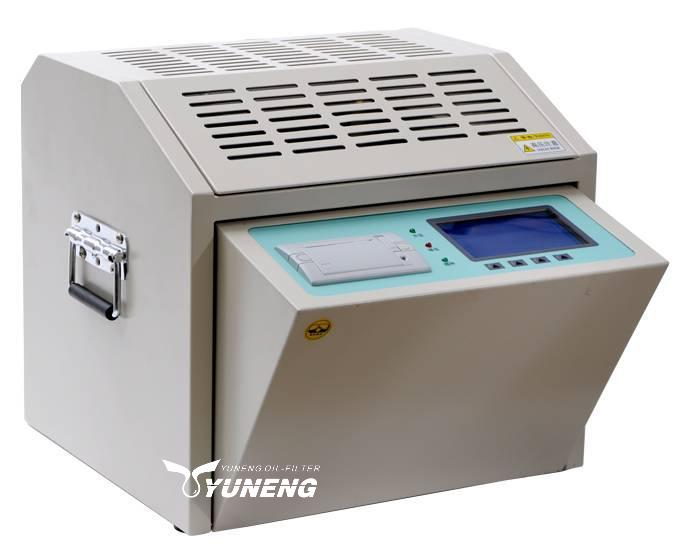
YUNENG Transformer Oil BDV Tester

The YNHYG-A Series IEC Standard Transformer Oil BDV Tester explored by YUNENG emerges as a self-contained solution for assessing the health of insulating oil in transformers. Built to comply with international (IEC-156) and national (GB507-86) standards, it leverages microprocessor control for automated testing, minimizing errors and simplifying operation. This user-friendly design, coupled with its portability, makes it ideal for both field and lab environments.
The YNHYG-A Series IEC Standard Transformer Oil BDV Tester boasts several notable features:
- The device offers automated detection capabilities, streamlining the testing process.
- Equipped with a compact TPU-A panel printer, the tester facilitates the automatic printing of test results, ensuring efficient documentation.
- Users can customize testing parameters such as testing times, stirring duration, and stationary time, enhancing flexibility and accuracy. Sound and light controls provide alerts for continuous printing and non-printing phases.
- Incorporating full automatic magnon technology, the tester ensures reliable and precise testing outcomes, contributing to enhanced efficiency and performance.
Whether you’re a seasoned professional or seeking a reliable BDV testing solution, exploring the YNHYG-A Series in greater detail is recommended.






