How SF6 Gas Treatment Supports Compliance Under the EU Ban After 2026
Table of Contents
Sulfur hexafluoride (SF6) is a common choice for medium-, high-, and extra-high-voltage switchgear as the insulation and arc-quenching gas. However, with the number of global warming potential (GWP) values of around 24,300, SF6 is currently the focus of strict regulatory measures, especially the EU F-gas Regulation (EU) 2024/573.
The rule does not prohibit the use of SF6 in new electrical equipment immediately via a voltage-dependent phased banning system, unlike sudden bans. As a matter of fact, this measure, step by step, changes the way maintenance, refurbishment, and the management of asset life-cycle must be planned by utilities, EPC contractors, and equipment owners.
In this situation, SF6 gas purification, which is based on modern SF6 gas vacuum pumps and SF6 gas refining machines, is turned into an important compliance and sustainability strategy rather than a regular maintenance job.
Understanding the SF6 Ban: Voltage Levels and Effective Dates
Not all types of equipment are affected by the EU regulation in the same way. Rather, it is centred on low-voltage systems first and then spreading to higher voltage classes, which might require longer validation cycles for technical alternatives.
SF6 Ban Timeline for New Switchgear (EU Market)
| Voltage Level | Rated Voltage Range | SF6 Ban Effective Date | Key Conditions |
| Medium Voltage (MV) | ≤ 24 kV | 1-Jan-26 | Full ban on SF6 in all new MV switchgear |
| High Voltage (HV) | 52–145 kV | 1-Jan-28 | Applies first to equipment with short-circuit current ≤ 50 kA |
| Medium Voltage (MV) | 24–52 kV | 1-Jan-30 | Covers remaining MV distribution systems |
| Extra-High Voltage (EHV) | > 145 kV | 1-Jan-32 | Includes large transmission and high short-circuit systems |
Key takeaway: While new equipment faces restrictions, existing (“installed base”) SF6-filled equipment remains operational for decades, shifting regulatory focus toward how SF6 is handled, not simply whether it exists.

Why SF6 Gas Treatment Becomes Mandatory After 2026
The regulation was primarily aimed at new switchgear, yet there was another critical aspect to it – after 2035, maintenance works could not be done utilizing new SF6 gas. Only recycled and purified SF6 gases shall be accepted.
This makes SF6 gas treatment essential for:
- Routine maintenance of existing GIS and circuit breakers
- Life-extension programs for HV and EHV substations
- Decommissioning and retrofitting projects
- Compliance audits and environmental reporting
Improper handling—venting, partial recovery, or contaminated reuse—now represents a direct regulatory and financial risk.
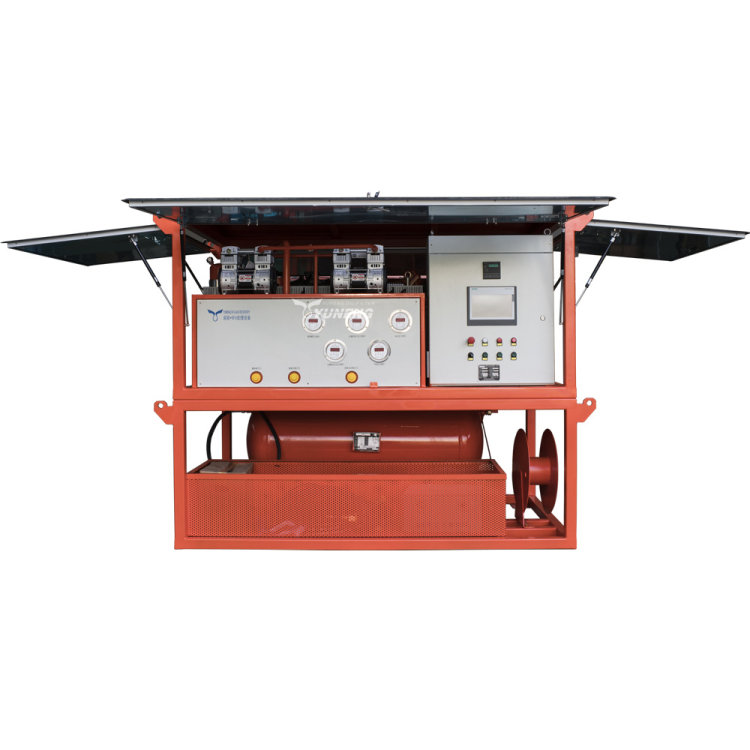
The Role of SF6 Gas Vacuum Pump Systems in Zero-Emission Operations
The SF6 gas vacuum pump is the central component of any SF6 gas treatment operation. Its function is to remove leftover gas from electrical compartments before accessing, maintaining, or removing the equipment.
As voltage rises, internal gas volumes and pressure stability demands will rise significantly, so that the vacuum performance will be a critical issue.
Key Performance Requirements Under Post-2026 Standards
Modern sf6 gas vacuum pump systems must deliver:
- Ultimate vacuum ≤ 1 mbar (0.1 kPa) to minimize residual SF6
- Oil-free dry pump designs, eliminating hydrocarbon contamination
- Multi-stage pumping capability for large GIS and EHV breakers
- Low leakage rates (<0.1% per year) to meet environmental audits
Compact dry vacuum pumps are ideal for quick service cycles on medium voltage equipment (≤24kV). On the other hand, huge vacuum systems are indispensable for uptime reduction with simultaneous compliance with even stricter emission limits for high and extra-high voltage setups.
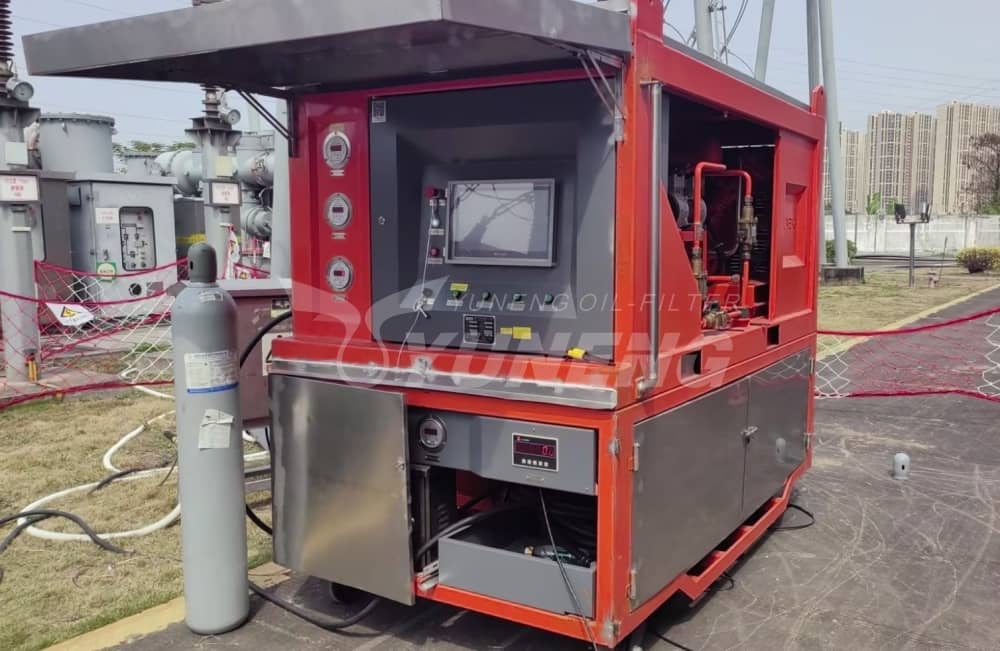

SF6 Gas Refining Machine: Turning Waste Gas into a Strategic Asset
Recovered SF6 gas is rarely reusable without treatment. Decomposition products—such as SO₂, SOF₂, HF, moisture, and air contamination—accumulate over years of operation, especially in high-load HV and EHV systems.
A modern SF6 gas refining machine enables utilities to:
- Restore degraded gas to ≥99.9% purity
- Meet IEC 60480 regenerated gas standards
- Eliminate the need for virgin SF6 procurement
- Support circular economy objectives
Core Refining Technologies
Advanced SF6 gas refining machines integrate:
1. Multi-stage filtration:
- Molecular sieves for moisture removal (dew point ≤ −40 °C)
- Activated alumina and carbon for acidic by-products
2. Cryogenic liquefaction and separation: Efficient separation of SF6 from air, N₂, or CF₄
3. Precision purity control: Output gas purity ≥ 99.9% by weight
These features are vital, particularly for HV (52-145 kV) and EHV (greater than 145 kV) equipment, where the quality of gas has a direct impact on the machine’s insulating materials and, hence, its long-term reliability.
Matching SF6 Treatment Strategies to Voltage Classes
1. Medium Voltage (≤24 kV) – Ban Effective 2026
Immediate transition to alternative gases in new equipment
Existing installations require:
- Compact sf6 gas vacuum pump units
- On-site or centralized SF6 gas treatment systems
- High maintenance frequency makes fast recovery cycles essential
2. High Voltage (52–145 kV) – Ban Effective 2028
Large installed base remains operational well beyond 2030
Requires:
- High-capacity vacuum pumping systems
- Industrial-grade SF6 gas refining machines
- Emphasis on gas purity to maintain insulation margins
3. Extra-High Voltage (>145 kV) – Ban Effective 2032
- Long asset lifespans (40–50 years)
- Extremely high gas volumes per compartment
- Demands:
- Multi-stage vacuum and recovery systems
- Advanced refining to avoid costly gas replacement
- Redundant monitoring and digital compliance records

Digital Compliance: The New Invisible Requirement
Beyond physical performance, EU regulations increasingly emphasize traceability and documentation.
Modern SF6 gas treatment systems must support:
- Integrated mass flow meters or electronic weighing (±0.1 kg accuracy)
- Automatic logging of:
- Initial pressure
- Final vacuum level
- Recovered gas mass
- Refined gas purity
- Exportable digital reports for regulatory audits
This digital layer transforms SF6 handling from a maintenance task into a regulated, auditable process.
Industry Outlook: From Product Sales to Lifecycle Services
The phased SF6 ban does not eliminate SF6 overnight. Instead, it reshapes the market around lifecycle management, where technology providers compete on:
- Vacuum efficiency
- Refining depth and gas recovery rates
- Compatibility with future alternative gases (C4-FN, C5-FK blends)
- Data transparency and compliance readiness
In this environment, investments in sf6 gas vacuum pump systems, SF6 gas treatment solutions, and SF6 gas refining machines are no longer optional—they are strategic assets for grid operators navigating the transition to low-carbon power infrastructure.
Conclusion
The EU’s voltage-based SF6 ban timeline makes one reality clear: SF6 management is shifting from installation decisions to long-term operational discipline.
Since 2026, besides the kind of SF6 use, compliance will also be about the treatment, refining, documentation, and rate of SF6 gas recovery in a machine. It is the companies that make their SF6 gas treatment system up-to-date that will be in the lead to follow the rules, survive the financial loss, and contribute to the global decarbonization target without at the same time disturbing grid reliability.

FAQ
Q1: How does investing in an SF6 gas refining machine reduce operating costs?
An SF6 gas refining machine is available that purifies and reuses contaminated or aged SF6 to ≥99.9% purity, thereby eliminating repeated purchases of virgin gas.
Refining can reduce the lifecycle gas costs by 40-70% for high- and extra-high-voltage equipment with large gas volumes. This will also be a way to adhere to the future restrictions on the use of virgin SF6.
Q2: What specifications should be prioritized when sourcing SF6 gas handling equipment?
- Oil-free sf6 gas vacuum pump systems (to avoid gas contamination)
- Refining systems compliant with IEC 60480
- High recovery efficiency (≥99.9%)
- Digital logging and audit-ready documentation
Q3: Why is oil-free vacuum technology recommended for SF6 recovery?
Oil-sealed pumps can introduce hydrocarbons into recovered SF6, making it unsuitable for reuse or refining.
The oil-free dry SF6 gas vacuum pumps play a role in eliminating subsequent pollution, also help in improving the gas quality and lessening the work of the following SF6 gas refining machines, which are mostly used in HV and EHV GIS systems.
Q4: When should recovered SF6 be refined instead of reused directly?
If the gas shows elevated moisture, acidic by-products, or air contamination—common in long-service or heavily loaded equipment—it must be processed through an SF6 gas refining machine.
Refining ensures dielectric strength is restored and prevents insulation failure after refilling.






